Are you struggling with severe chronic pain? You need not worry anymore as there is a revolutionary device called the TENS/EMS unit, that combines two distinct therapies to provide you with quick and lasting pain relief.
In this guide, you will get to know how this device works and its immense potential in providing drug-free and non-invasive treatment.
TENS/EMS units are electrical muscle stimulation devices used in physical therapy and pain management. The initials “TENS” stand for “transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation,” and the device works to stimulate nerve fibers with low-voltage electric pulses to help block pain signals from reaching the brain. The second element of a TENS/EMS unit is EMS (electronic muscle stimulation), which uses electrical currents to contract and relax muscles that cannot be voluntarily controlled by the patient. Combining these two therapies into one device creates an incredibly effective solution for pain relief.
The TENS/EMS unit has become a very popular tool in physical therapy, chronic condition management, injury rehabilitation, pre or post-operative care, and other medical applications. Because of its many potential benefits, more individuals are investing in personal use models so they can benefit from this versatile therapy in their own home or on the go.
This guide will provide an overview of TENS/EMS technology as well as explain how it can be used effectively for long-term pain relief and injury rehabilitation. It will answer frequently asked questions about different types of units available on the market as well as provide general safety information while using the device yourself at home or elsewhere. Finally, it will discuss strategies for those wondering “when” to use such technology for therapeutic care instead of prescribed medications or other more invasive treatments.
Explanation of TENS EMS Unit and its purpose
The Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) & Electrical Muscle Stimulator (EMS) unit is a pain relief device which uses two different therapies to provide physical therapy for a variety of conditions. TENS works by delivering electrical current through electrodes placed on various locations on the skin in order to reduce the pain associated with muscles, joints, and connective tissues. EMS stimulates targeted muscles through electrical impulses to improve the function of weakened or injured muscle groups. Both therapies help to reduce pain, speed up healing and increase mobility.
The TENS EMS unit is becoming increasingly popular as they are scientifically studied technologies that can be used safely over an extended period with excellent results. It’s easy to use and non-invasive which makes it appealing for those who prefer an alternative form of physical therapy or need immediate relief from acute pain due to injury or inflammation. The use of the TENS & EMS unit has been proven to reduce inflammation, promote circulation and overall relaxation by reducing high levels of stress hormones in the blood stream.
TENS & EMS units also offer localized treatment for more targeted relief, making them ideal for treating specific areas that are causing discomfort and stiffness such as neck pain, lower back pain, headaches management and knee pain. The device is also used by physical therapists to help strengthen muscles by contracting them with defined frequency patterns – something not possible with manual stretching or exercise alone. By helping relieve muscle spasms while activating neglected muscles it helps improve strength endurance while decreasing swelling and improving overall joint range of motion.
This guide provides a complete overview of what’s needed to get started using this device as well as tips on selecting the best option based on individual needs, how it works its therapeutic benefits and safety precautions including potential side effects that may arise when using this device over an extended period such as skin irritation from electrodes pads but can easily be addressed when using appropriate accessories. An explanation of how to adjust settings according different types body positions is included along with other do’s and don’ts advice when using the device so you may receive optimal results from your treatment sessions safely without unnecessary risks associated with incorrect usage.
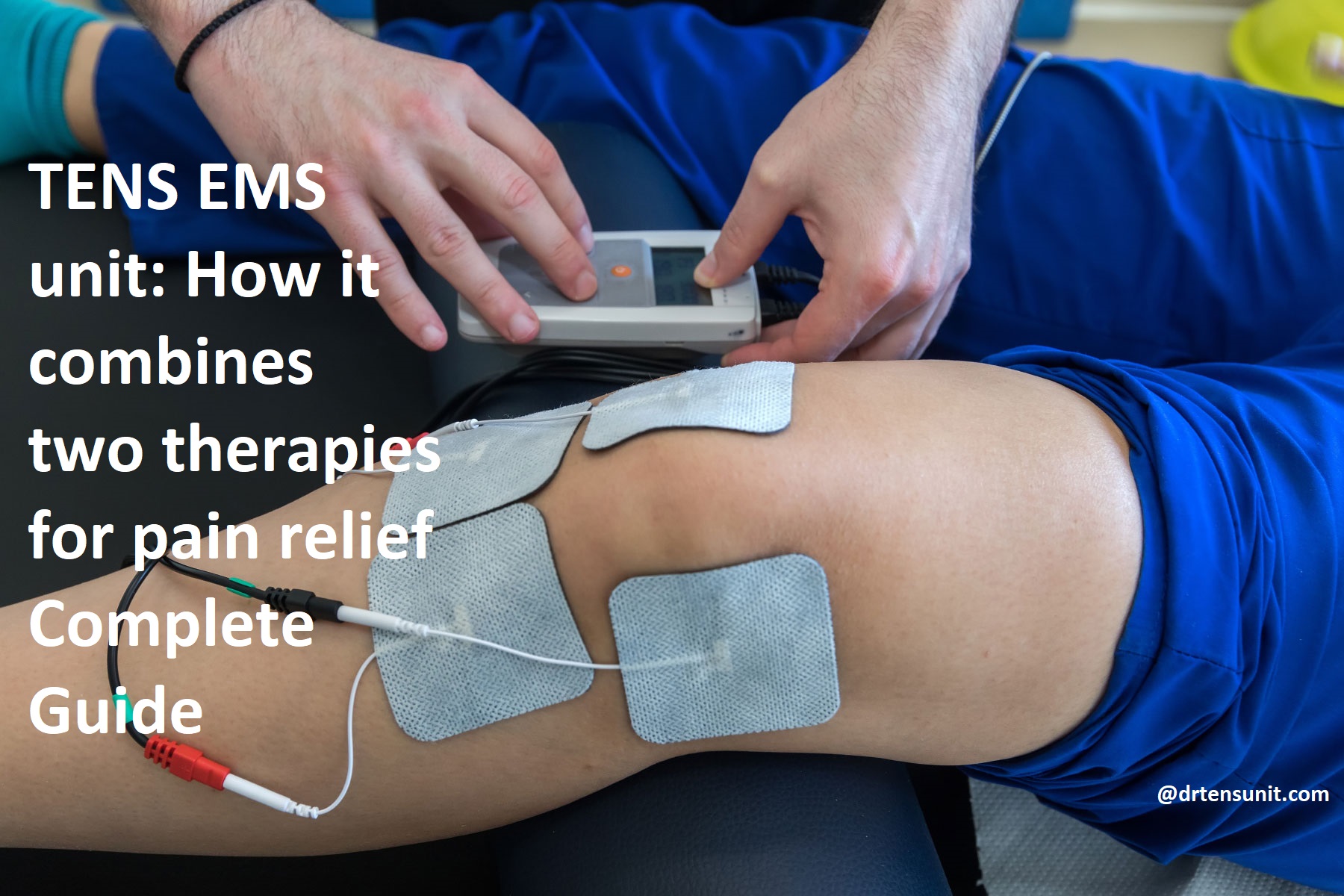
Brief overview of TENS and EMS therapies
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) are two types of pain relief therapies that can be used alone or together. TENS is the process of sending mild electrical signals to the affected area, stimulating nerve fibers and blocking pain signals sent to the brain.
EMS is a similar process but involves using higher voltage to stimulate muscle contraction, helping with muscle strengthening and aiding in rehabilitation from injuries or chronic conditions.
Combining these therapies can create an incredibly powerful tool for pain relief and muscle training. TENS causes muscles to relax, decreasing pain in the area, and EMS helps to rehabilitate those same muscles by assisting with strength training. This combined treatment is commonly referred to as TENS/EMS therapy, and has been found to bring long-term relief from chronic pain symptoms when used regularly.
By understanding how these treatments work individually and together, you can get a full picture of why this type of therapy has become so popular among athletes, physical therapists, and those dealing with chronic health conditions such as arthritis or back pain. Having knowledge on this important topic can help equip you with various tools for managing your personal health journey!
TENS Therapy
TENS, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, is a pain relief therapy that uses low voltage electrical current to stimulate nerve endings, block pain signals and offer relief. TENS devices are small enough to be worn beneath clothing and typically used for localized treatments in specific areas. They have adhesive pads with electrodes that attach directly to the skin, delivering low-voltage electrical stimulation through the body’s nervous system. These waves differ in shape and frequency according to the type of current being delivered.
The type of waves the machine delivers affects how it feels on your skin and what kind of effect it gives you. The most common types are sine waves and pulsed square BoraKempf Therapy (BKT)waves. Sine wave currents have gentle, rolling patterns that cause a deep massage-like sensation, while pulsed square BoraKempf Therapy (BKT)wave currents are higher intensity, fast pulses more likely to provide quick relief from acute pain.
When using TENS therapy, users gradually increase their threshold setting until they reach comfortable levels of relief while remaining aware of potential side effects such as irritation at the site where electrodes were placed or an increased sensitivity to touch after exposure due to their nerves becoming accustomed to the current run through them during treatment sessions.
What is TENS therapy?
TENS, which stands for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, is a type of therapy that uses low voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief. It has been used for treating muscle and joint pain for decades, with the biggest benefits being seen in the areas of chronic pain management, tendonitis relief and sports-related injuries.
TENS is based on the principals of gate control theory. This theory suggests that electric current applied to a specific area of the body will interfere with or “block” signals coming from the brain that ultimately lead to pain sensation. Theoretically, low voltage electrical current sent through electrodes placed on areas suffering from pain will “override” signals sent by our brains telling us we are in pain, providing temporary but effective relief.
The TENS unit itself consists of small battery powered device connected to adhesive electrodes via wires. The electrode pads are typically placed on the surface of skin over and near areas in which you would like to address discomfort or more specifically; they should be placed as close as possible to your source of pain without irritating it further. Electricity is then conducted through these electrodes at various frequencies and intensities depending on what works best for your particular situation.
When using a TENS unit, it is important to keep the current intensity low enough that it provides patient comfort; but high enough so it produces an effective neurotransmission blockade leading to temporary analgesia (pain relief). As long as this balance between intensity and comfort is maintained both therapeutic effectiveness and safety can be achieved simultaneously.
How does TENS therapy work?
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) therapy is a non-invasive, drug-free method of providing pain relief through the application of electrical impulses to the nerves and surrounding tissue.
A TENS unit is a small, portable device worn on the body that emits tiny electrical pulses through electrodes placed at the source of pain. The electrical current generated by these pulses helps your muscles to relax and increases your body’s natural production of endorphins – chemicals that block pain signals from being sent to your brain. This encourages healing within your muscles as well as reducing inflammation and swelling. Additionally, TENS also causes an increase in blood flow which can also help promote faster muscle recovery.
With regular use, you may find that you experience lasting relief from chronic pain and improve overall quality of life.

Types of TENS Units
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) units utilize electrical current to relieve pain in a variety of applications. TENS offers a non-invasive, drug-free option to managing pain. Combining electrical stimulation therapy with EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) technology, TENS EMS units can provide users with superior pain relief.
A few types of TENS units include:
Standard TENS Units: Standard TENS has been the go-to option for those suffering from muscle and joint aches and pains. Standard units emit low-voltage electrical currents that help to reduce inflammation and increase circulation in the area being treated by stimulating nerve cells.
Dominant Frequency Waveform Unit: Dominant frequency waveform is an advanced form of nerve stimulation that utilizes a continuous pulsed waveform, which helps to facilitate healing by sending rhythmic signals to the muscles and nerves in order to produce positive clinical results in the shortest amount of time possible.
Intensity Modulated Stimulation Unit: Intensity modulated stimulation (IMS) is an advanced variation on traditional TENS treatments but utilized pulses with different lengths and intensities instead of just electrical current, allowing for increased effectiveness without any additional discomfort or side effects when compared to basic TENS treatments.
Microcurrent Enhancement Unit: Microcurrent enhancement is an extremely low voltage electrical current, often too low (on the microampere level) for users to even notice it flowing through their bodies during treatment sessions. In addition to helping reduce inflammation, this type of unit may even help improve oxygen uptake at specific locations throughout the body by increasing circulation, resulting in more healthy tissue and faster healing times for underlying conditions as well as general injury prevention and maintenance needs.
Benefits and Risks of TENS Therapy
TENS or Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Therapy is a non-invasive, pain relief therapy used by physical therapists, chiropractors and other healthcare professionals to reduce the patient’s pain. The device works by sending small electrical impulses through the patient’s skin using electrodes placed on the surface of the skin. These pulses interact with nerve fibers in the area being treated and suppress pain by blocking out pain signals from traveling to the brain.
The TENS treatment can provide immediate relief for back, neck and lower extremity muscle and joint pain as well as headaches due to migraines or TMJ. It is thought that TENS also offers long-term benefits such as reducing inflammation and promoting healing at the affected site. However, further research is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Although TENS treatments are generally safe, there are some risks associated with their use including: skin irritation due to electrode placement; discomfort due to electric current; interference with other medical devices such as pacemakers; potential increases in nerve sensitivity which can result in increased discomfort; and an increased risk of infection from improper electrode placement or cleaning. It is important for patients to discuss these risks with their healthcare professional before undergoing a TENS treatment course.
EMS Therapy
Electrical Muscular Stimulation, referred to as E-M-S, is physical therapy treatment that uses electrical impulses to contract and relax muscles. This contraction helps to build strength in the affected muscles and can be used in physical rehab, sports training and pain relief.
EMS is often beneficial during the healing process when a client has limited range of motion and muscle spasms. Additionally, it may be used as an adjunct therapy for clients with nerve injuries.
During a typical EMS session, the patient lies on their back or stomach while electrodes are applied directly to the skin in order to deliver small doses of electricity into specific muscles. Depending on the type of treatment being received and current level of immunity, the therapist may adjust to different intensity levels. In each session, electrical pulses are distributed through both sides of the targeted area at various depths from shallow pulsing at low intensity levels up to stronger pulses that can penetrate deep within tissue layers.
EMS therapy encourages muscular activation through a healthy contractile response resulting in improved functional recovery. When applied properly, EMS can also help maximize muscle performance by further developing motor control for efficient recruitment and movement patterns seen during regular daily activities or sporting events alike. It has been successfully utilized for improving posture awareness and coordination due to its ability to trigger corrective neuromuscular responses from multiple planes of motion within each system it stimulates. Through repetitive progressive neuromuscular stimulation, it assists with maintaining proper joint stabilization encouraging healthier human movements thus reducing risk of injury while simultaneously optimizing sports performance goals quickly & safely.
What is EMS therapy?
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) therapy is a type of pain relief treatment that uses electrical pulses to stimulate the body’s muscles to contract and relax. It is an effective way of relieving pain, reducing inflammation and improving circulation.
This type of therapy has been used for decades worldwide, and it is a safe and non-invasive form of therapy for many ailments. EMS works by creating controllable electrical charges that are delivered directly to the targeted muscle groups, causing them to contract or relax in order to relieve tension.
EMS is most commonly used for treating chronic pain, limited range of motion, increased flexibility, and rehabilitation from injuries or surgery. It can also be used as a preventative measure since it improves circulation throughout your body.
The FDA approved use of EMS devices as a form of medical treatment in 1983 – proving its effectiveness over time.
How does EMS therapy work?
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) is a therapeutic modality used to help people suffering from pain or muscle spasms. During it, pain-relieving electrical pulses are sent through electrodes to the muscles and their nerve fibers, stimulating them and providing relief from soreness, tension, and tightness.
The strength and frequency of the electrical pulses depend on the individual’s condition and needs; typically, those with chronic pain opt for higher frequencies in order to fully enjoy the benefits of this therapy. EMS therapy works by triggering muscle contractions that not only reduce discomfort but also support muscle strengthenining. It also increases blood flow, oxygen levels and nutrients to targeted areas of our body, helping to speed up cell regenerations in affected areas.
Moreover, EMS therapy can be used both therapeutically and as a preventative tool against injury or damage. As such, not only can it reduce existing aches and pains but also prepare one’s body for physical activities or stretching routines that could otherwise cause harm or an uncomfortable experience. Additionally, individuals use EMS therapy as part of their rehabilitative treatment after having suffered a sports injury or other type of trauma that forced them to stay still for a long period of time.
Types of EMS Units
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) units are devices that use electrical current to stimulate muscle contractions, as well as other treatments. The two main types of EMS are Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), which is used to relieve pain, and Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS), which is used to target muscles and thus help increase their strength. These two types of treatments can be combined in one unit, referred to as a TENS EMS unit.
TENS EMS units are ideal for addressing acute or chronic pain, sciatica and neuralgia, athletic performance improvement, physical therapy, reflexology and more. They can help reduce swelling, improve circulation and ease muscle spasms while also providing targeted stimulation of deep muscle tissue. This allows users a wide range of therapeutic options with greater control over their treatment regimen than ever before possible.
A TENS EMS unit typically consists of an interface device such as a control box or app from where the user can customize settings such as current amplitude and waveform type; electrode contact pads; output cables for connecting the electrodes to the device; battery or mains power; skins adhesive tapes for secure electrode placement; optional carry case depending on make & model; charger(s). Depending on the brand/model chosen additional components may also be included such as wired or wireless remotes for easy access during using. By combining two types of therapy in one session this device provides users with effective treatment results in a short amount of time.
Benefits and Risks of EMS Therapy
Electric muscle stimulation (EMS) therapy is rapidly gaining popularity as a non-invasive, drug-free treatment of various muscular and pain related issues. EMS therapy delivers mild electrical impulses to muscles, allowing the muscles to contract and relax at different intensities, which in turn reduces pain, increases blood circulation and improves mobility.
The three primary benefits associated with EMS therapy include:
– Pain Relief: By using lower frequency signals it can stimulate the release of natural anesthetics endorphins as well as reduce spasms and cramping in skeletal muscles. – Increased Strength: By stimulating muscle fibers, it generates a reaction in the body that leads to improved muscle strength over time. – Improved Circulation: It helps improve nerve conduction speeds that energize injured or weak muscles along with increasing local blood flow which aids in accelerating repair of soft tissue injuries.
Although there are numerous reported medical benefits associated with EMS therapy, it’s important to be aware of potential risks that may exist when using an electrical muscle stimulator such as skin irritation or burns caused by excessively strong currents or leaving the electrodes on for too long. To avoid side effects, make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions for use and consult a professional if you have any questions about the type or intensity of impulses being used.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Combining TENS and EMS therapy offers many potential benefits. For those looking for more permanent solutions to chronic pain and muscle injuries, these technologies offer a versatile way of managing the underlying root issues. The vast spread of features also ensure that both therapies can be used with different strengths to target individual requirements according to specific patient needs.
For those who are confused about what kind of therapy to use for their pain condition, there is no one-size-fits all answer — but combining the two may be worth considering. TENS and EMS therapy should always be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional or doctor, since you may have particular conditions that could make this kind of treatment unsuitable or too strong for your body. With optimal settings and advice from experts, a TENS & EMS unit can provide an effective tool for pain relief as well as helping people gain back control over their lives.
FAQ’s
What is a TENS EMS combo unit?
A TENS EMS combo unit is a device that combines Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) therapies in one machine.
What are the main methods that a TENS machine uses to provide you with pain relief?
TENS machine uses electrical impulses to stimulate the nerves and reduce pain sensation. It may also trigger the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural painkillers.
Can you use 2 TENS machines at the same time?
It is not recommended to use two TENS machines at the same time because it may interfere with the electrical signals and cause skin irritation or burns.
How does TENS and EMS work?
TENS and EMS work by using electrical impulses to stimulate the nerves and muscles. TENS is used for pain relief while EMS is used for muscle stimulation, rehabilitation, and strengthening.
Can I use EMS everyday?
It is safe to use EMS every day but with caution and according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Overusing EMS may lead to muscle fatigue, soreness, or injury.
Is EMS stronger than TENS?
EMS is stronger than TENS because it targets the muscles directly, while TENS targets the nerves. EMS is used for muscle stimulation, rehabilitation, and strengthening, while TENS is used for pain relief.
How does EMS stimulation work?
EMS stimulation works by sending electrical impulses to the muscles through electrodes attached to the skin. These impulses cause the muscles to contract and relax, which helps to strengthen and tone them.
How does EMS work?
EMS works by sending electrical impulses to the muscles through electrodes attached to the skin. These impulses cause the muscles to contract and relax, which helps to improve blood flow, relieve muscle tension, and improve muscle strength.
Does EMS burn fat?
EMS alone does not burn fat, but it can help to strengthen and tone the muscles, which can increase metabolism and burn fat when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
What are the side effects of EMS?
Some possible side effects of EMS include skin irritation, muscle soreness, muscle fatigue, or muscle spasms. It is important to use EMS according to the manufacturer’s instructions and under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
See Also:
- Best tens unit for back pain
- Best tens unit
- Best tens ems unit
- Best rechargeable tens unit
- Best portable tens unit

